GMI小孢子靈芝免疫調節蛋白質結合多種創新技術,
己取得結構,檢驗與多種應用專利,同時持續累積發表學術文獻並取得多項國際認證。
Abatract
Background
Cancer metastasis is a major cause of cancer-related deaths, emphasizing the urgent need for effective therapies. Although it has been shown that GMI, a fungal protein from Ganoderma microsporum, could suppress primary tumor growth in a wide spectrum of cancer types, it is still unclear whether GMI exhibits anti-metastasis properties, particularly in lung cancers. Further investigation is needed.
Aims and objectives
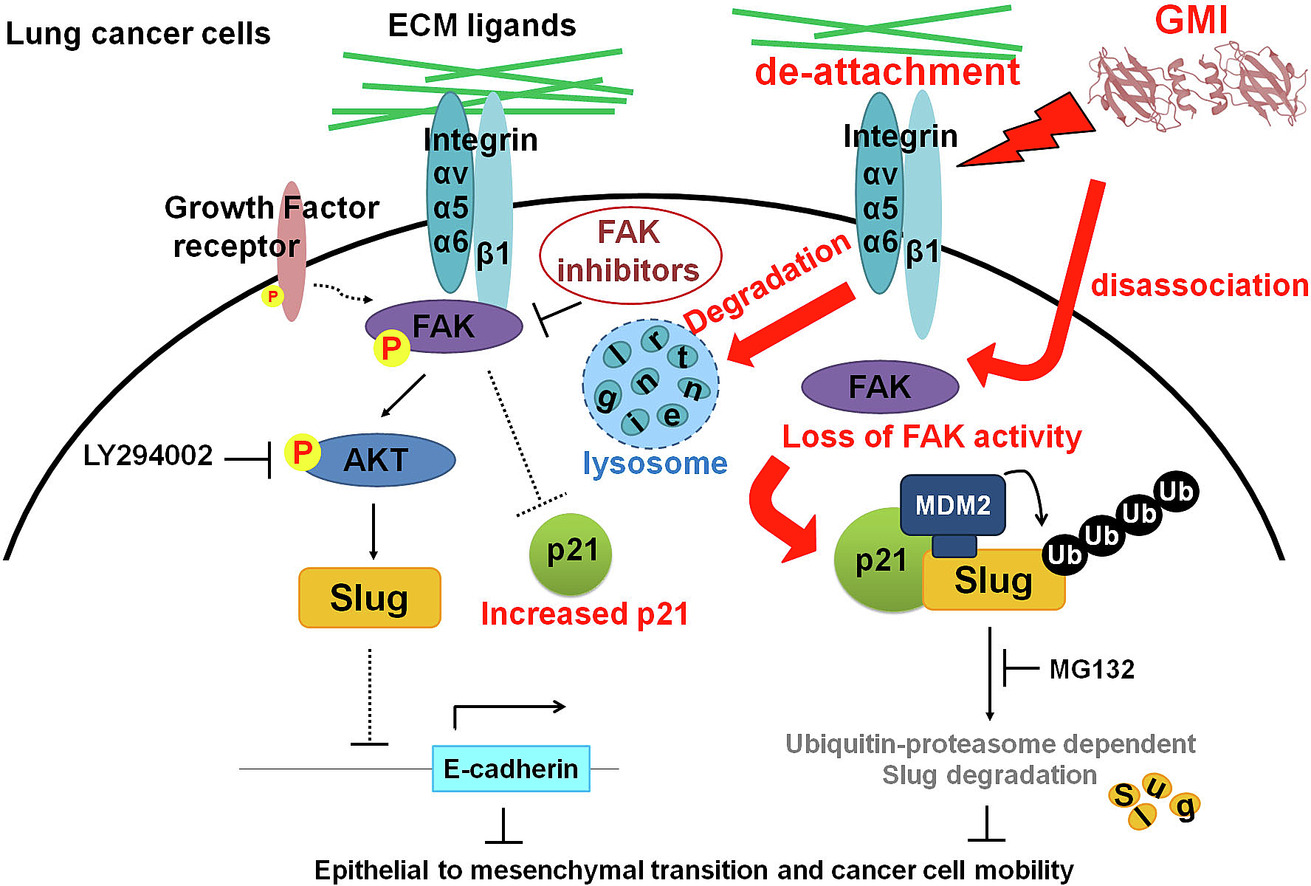
Cancer metastasis is a major cause of cancer-related deaths, emphasizing the urgent need for effective therapies. Although it has been shown that GMI, a fungal protein from Ganoderma microsporum, could suppress primary tumor growth in a wide spectrum of cancer types, it is still unclear whether GMI exhibits anti-metastasis properties, particularly in lung cancers. Further investigation is needed. Aims and objectives: The objective of this study is to investigate the potential inhibitory effects of GMI on lung cancer metastasis in vivo. Utilizing systematic and comprehensive approaches, our research aims to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms responsible for the anti-metastatic effects.
Materials and methods
In vitro migration and cell adhesion assays addressed the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related phenotype. Proteomic and bioinformatic analyses identified the GMI-regulated proteins and cellular responses. GMI-treated LLC1-bearing mice were analyzed using IVIS Spectrum to assess the anti-metastatic effect.
Key findings
GMI inhibits EMT as well as cell migration. GMI disrupts cell adhesion and downregulates integrin, resulting in inhibition of phosphorylated FAK. GMI induces macropinocytosis and lysosome-mediated degradation of integrin αv, α5, α6 and β1. GMI downregulates Slug via inhibition of FAK activity, which in turn enhances expressions of epithelial-related markers and decreases cell mobility. Mechanistically, GMI-induced FAK inhibition engenders MDM2 expression and enhances MDM2/p21/Slug complex formation, leading to Slug degradation. GMI treatment reduces the metastatic pulmonary lesion and prolongs the survival of LLC1-bearing mice.
Significance
Our findings highlight GMI as a promising therapeutic candidate for metastatic lung cancers, offering potential avenues for further research and drug development.